Bronchiolitis Obliterans
This information was reviewed and approved by Cecile S. Rose, MD, MPH (5/1/2025).
- Do not delete this
What is Bronchiolitis?
In bronchiolitis, inflammation or swelling causes obstruction in the smallest airways in the lungs. The bronchi (airways) are like the branches on a tree. As the air proceeds through the bronchi, these branches get smaller and smaller.
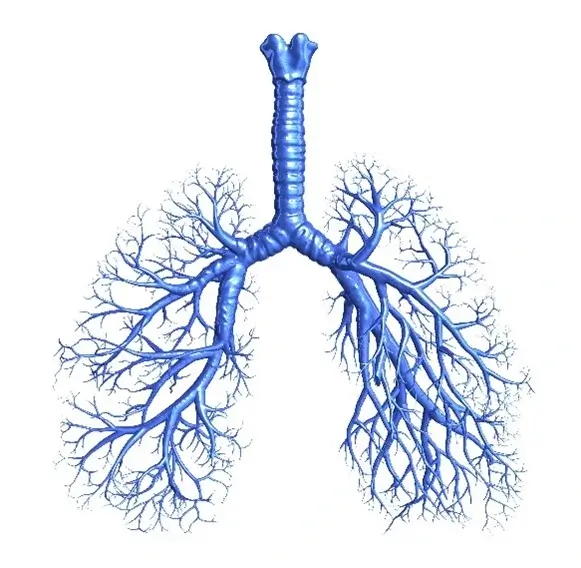
The bronchioles are the smallest airways. The bronchioles may become inflamed, and then scarred, by a number of causes.
Doctors identify different types of bronchiolitis by examining lung tissue under a microscope. These include constrictive, obliterative (referred to as bronchiolitis obliterans), proliferative, lymphocytic or respiratory bronchiolitis. Identifying the type of bronchiolitis may help determine the best prevention and treatment.
Some forms of bronchiolitis, such as obliterative bronchiolitis following a lung transplant, can be fatal if not treated. However, depending on the type and cause, the prognosis for this condition can range from mild to severe impairment. Some people with bronchiolitis may have mild impairment and slow progression, and others may have irreversible but stable disease.
Communicating with your health care provider will help create a comprehensive treatment plan.
Causes
The bronchioles are the smallest airways. The bronchioles may become inflamed and scarred by a number of causes. Inflammation and scarring from bronchiolitis may occur as a result of:
- Autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis)
- Bone marrow, lung or heart transplants
- Inflammatory bowel disease (e.g., ulcerative colitis)
- Medication reactions
- Respiratory infections
- Smoking or vaping (known as respiratory bronchiolitis)
- Inhalational exposures, including:
- Irritants such as chlorine, ammonia, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxides
- Flavoring chemicals such as diacetyl used in the production of butter-flavored popcorn and coffee roasting
- Vaping flavored e-liquids
- World Trade Center (WTC) dust
- Particulate matter from post-9/11 military deployment to Iraq, Afghanistan and Southwest Asia
- Mineral dusts (e.g., coal mine dust, silica, asbestos)
If a cause is not identified it is called idiopathic bronchiolitis. A specific form known as panbronchiolitis has been described in association with sinusitis. This occurs most often in men. It typically responds to treatment with special antibiotics.
It is important to identify a cause of the bronchiolitis to help determine the best treatment.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptoms of bronchiolitis are a dry cough and shortness of breath. The earliest symptom may be shortness of breath especially with exertion or strenuous activity. For example, you may notice shortness of breath only when running or hurrying to catch a bus. Later, you may notice shortness of breath when casually walking across the street. The cough may be dry, hacking and persistent. Fatigue and wheezing also may occur. These symptoms may be noticeable within days to weeks after some inhalation exposures or respiratory infections. Symptoms may not occur until months or years after organ transplant or after some particulate/chemical exposures.
Your health care provider will evaluate all your symptoms as part of managing your bronchiolitis.
If left untreated, symptoms of bronchiolitis may progress, causing further damage to the airways in the lungs.
Diagnosis
A complete medical and exposure history is essential for diagnosis. Your doctor will conduct a complete physical exam and ask you questions about your lifestyle, including your family history, your job, your habits, your hobbies, your current medications and your symptoms. When bronchiolitis obliterans is suspected, your doctor may have you do a number of tests.
Breathing and Exercise Tests
Spirometry: A spirometry test measures airflow in and out of the lungs. This indicates whether or not there is airway narrowing that obstructs the flow of air in and out of the lungs. Spirometry test results are useful in making the diagnosis of a class of lung disorders. Even more important, yearly spirometry measurements help to detect lung disease at an early stage when lifestyle changes and treatment may help forestall future problems.
Imaging Tests
CT scan of the chest: A CT or CAT scan is a shortened name for computerized tomography. During a CT scan of the chest, detailed pictures are taken of cross sections or slices of the thoracic structures in your body. Thoracic structures include your lungs, heart and the bones around these areas. Sometimes intravenous contrast is administered to better see the blood vessels in the lung. Chest CT scan findings in bronchiolitis may be subtle. They often show markers of small airway inflammation (such as air trapping, tiny nodules and a thickening of bronchial walls).
X-rays: X-rays can show irregularities or damage in the lungs caused by bronchiolitis. You doctor may verify a diagnosis, or evaluate what other diseases or conditions may be present with other tests.
Procedures
A surgical lung biopsy is the most definitive way to diagnose bronchiolitis. During a biopsy a small amount of tissue is taken from a specific area of the lung. The cells and tissue can be studied closely to help determine your diagnosis and the best treatment. There are different surgical approaches for biopsy depending on the location.
You and your health care provider may choose to have you seen by a specialist, such as a pulmonologist (lung specialist) to confirm a diagnosis and treat your bronchiolitis once it’s diagnosed.
Treatment
Managing bronchiolitis includes partnering with your health care provider to create a comprehensive treatment plan.
Several forms of bronchiolitis are not reversible. Treatment of some forms, such as bronchiolitis due to a lung transplant or autoimmune disease, can help to stabilize or slow progression. For that reason, it is important to recognize bronchiolitis early because intervention in the late stages of disease may prove ineffective.
Medications
Treatment usually involves medication, primarily the use of corticosteroids. In some cases, immunosuppressive medications, which decrease the body's immune response, and lung transplants are used to treat the disease. Some studies suggest that a class of antibiotics known as macrolides (e.g., azithromycin) may improve symptoms and lung function in people with panbronchiolitis.
Talk to your doctor about managing your medications.
Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy may be prescribed based on oxygen testing. If oxygen is prescribed, it is used to normalize the oxygen level in blood during sleep, rest and activity.
In the case of inhalational exposures, removal from the causal environment is crucial to controlling progression of the disease. For respiratory bronchiolitis, smoking and vaping cessation is essential.
Lifestyle Management
Living a healthy lifestyle is important when dealing with bronchiolitis. Positive lifestyle changes could include:
- Regular exercise
- Healthy eating
- Breathing retraining
- Avoiding infections (and getting recommended vaccinations)
- Giving up smoking and vaping (cigarettes, cigars, pipes, marijuana, e-cigarettes)
- Support from others
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials help determine new treatment options for diseases and conditions. Patients with bronchiolitis have access to clinical trials and should speak with their physician to determine what trials might work best for them.
See a Specialist
It’s important to be evaluated by a pulmonologist who specializes in bronchiolitis if you or a loved one:
- Has symptoms of bronchiolitis
- Would like strategies to help improve your current treatment of bronchiolitis
At National Jewish Health in Denver, Colorado, we have one of the world’s leading programs for dealing with lung diseases and infections resulting from environmental and occupational exposures. Learn more about our Environmental and Occupational Health program or use the button below to make an appointment.
 Clinical Trials
Clinical Trials
For more than 100 years, National Jewish Health has been committed to finding new treatments and cures for diseases. Search our clinical trials.
