A variety of prescribed topicals are available for eczema treatment, in addition to over-the-counter medications, such as various cream and ointment moisturizers. Medicines are added to your daily skin care when itching and rash from atopic dermatitis are not well controlled. Medication is also required if there is an infection.
Eczema Medication
Topical Steroids
.jpg) Steroid medicines that are applied to the skin are called topical steroids. Topical steroids are drugs that fight inflammation. They are very helpful when rash is not well controlled. Topical steroids are available in many forms for treatment of eczema such as ointments, creams, lotions, gels and even tape. It is important to know that topical steroids are made in low to super potent strengths. Do not substitute one topical steroid for another without your healthcare provider's advice. Used correctly, topical steroids are safe and effective treatment for atopic dermatitis. Steroid pills or liquids, such as prednisone, should be avoided because of side effects and because the rash often comes back after they are stopped.
Steroid medicines that are applied to the skin are called topical steroids. Topical steroids are drugs that fight inflammation. They are very helpful when rash is not well controlled. Topical steroids are available in many forms for treatment of eczema such as ointments, creams, lotions, gels and even tape. It is important to know that topical steroids are made in low to super potent strengths. Do not substitute one topical steroid for another without your healthcare provider's advice. Used correctly, topical steroids are safe and effective treatment for atopic dermatitis. Steroid pills or liquids, such as prednisone, should be avoided because of side effects and because the rash often comes back after they are stopped.
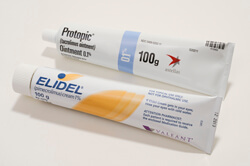 Topical Clacineurin Inhibitors (TCIs)
Topical Clacineurin Inhibitors (TCIs)
TCIs are also medicines that are applied to the skin for the treatment of eczema. They also treat inflammation, but are not steroids. TCIs don't cause steroid side effects. A common side effect of TCIs is skin burning. This is often not a long-lasting problem. TCIs include Protopic® ointment (tacrolimus) and Elidel® cream (pimecrolimus).
Topical PDE4 Inhibitors (PDE4)
A topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor (PDE4) is a medicine that is applied to the skin to treat inflammation, but is not a steroid. This is approved for children 2 years and older with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. PDE4s include Eucrisa® (crisaborole).
Biologics
This biologic is a medicine that is given as a routine shot. The is approved for adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. This biologic is Dupixent® (dupilumab).
Tar-based soaps and shampoos for Eczema
Skin and scalp products that contain coal-tar extracts have long been used to treat and reduce itching and rash. Tar shampoos, such as T-Gel®, are often helpful for red and itchy scalp. For scalp scaling or flaking, T-Sal® or Head and Shoulders® may be helpful.
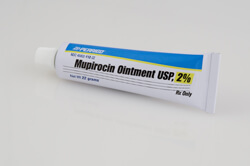 Anti-infectives
Anti-infectives
Skin infections caused by bacteria (e.g. impetigo), fungus (e.g. athlete's foot) and viruses (e.g. cold sores) can complicate the treatment of eczema symptoms. Some antibiotics, antifungal and antiviral medications are applied to the skin; others are pills or liquids taken by mouth. A skin infection can quickly get out of control. Call your healthcare provider right away if you think you have an infection.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines taken by mouth are used to control allergy symptoms and can help reduce itching from atopic dermatitis. Some antihistamines cause drowsiness. This can make you feel less itchy and help you sleep. Eczema creams and lotions that contain antihistamines or anesthetics (for numbing) should be avoided. They can cause skin irritation and allergic skin reactions.
Barrier Repair Creams for Atopic Dermatitis
Several topical products that are not FDA regulated, but require prescriptions since they are registered as medical devices, have been developed for the treatment of itchy rashes caused by eczema. These include Epiceram®, Atopiclair®, MimyX®.
Soak and Seal Therapy for Atopic Dermatitis
The soak and seal procedure is an effective treatment to retain moisture in dry, irritated skin as a result of eczema. Learn more.
Treating Skin Infections
Infections with bacteria and viruses are common among atopic dermatitis patients. Learn more.
Wet Wrap Therapy for Eczema
When eczema symptoms are severe, your healthcare provider may suggest wet wrap therapy. Learn more.
Phototherapy
Exposure to natural sunlight or ultraviolet light often helps people with atopic dermatitis. Learn more.
Psychological Counseling
People with eczema often struggle with a poor self-image and low self-esteem. In severe cases, the appearance of their skin can invite teasing and, especially with children, interfere with peer relationships. Learn more.
Day Hospitalization
Day hospitalization at centers specializing in treatment of eczema can be helpful for patients whose rashes are not controlled by medications and by avoiding irritants. Learn more.
 Clinical Trials
Clinical Trials

.jpg) Steroid medicines that are applied to the skin are called topical steroids. Topical steroids are drugs that fight inflammation. They are very helpful when rash is not well controlled. Topical steroids are available in many forms for treatment of eczema such as ointments, creams, lotions, gels and even tape. It is important to know that topical steroids are made in low to super potent strengths. Do not substitute one topical steroid for another without your healthcare provider's advice. Used correctly, topical steroids are safe and effective treatment for atopic dermatitis. Steroid pills or liquids, such as prednisone, should be avoided because of side effects and because the rash often comes back after they are stopped.
Steroid medicines that are applied to the skin are called topical steroids. Topical steroids are drugs that fight inflammation. They are very helpful when rash is not well controlled. Topical steroids are available in many forms for treatment of eczema such as ointments, creams, lotions, gels and even tape. It is important to know that topical steroids are made in low to super potent strengths. Do not substitute one topical steroid for another without your healthcare provider's advice. Used correctly, topical steroids are safe and effective treatment for atopic dermatitis. Steroid pills or liquids, such as prednisone, should be avoided because of side effects and because the rash often comes back after they are stopped. Topical Clacineurin Inhibitors (TCIs)
Topical Clacineurin Inhibitors (TCIs) Anti-infectives
Anti-infectives